Table of Contents
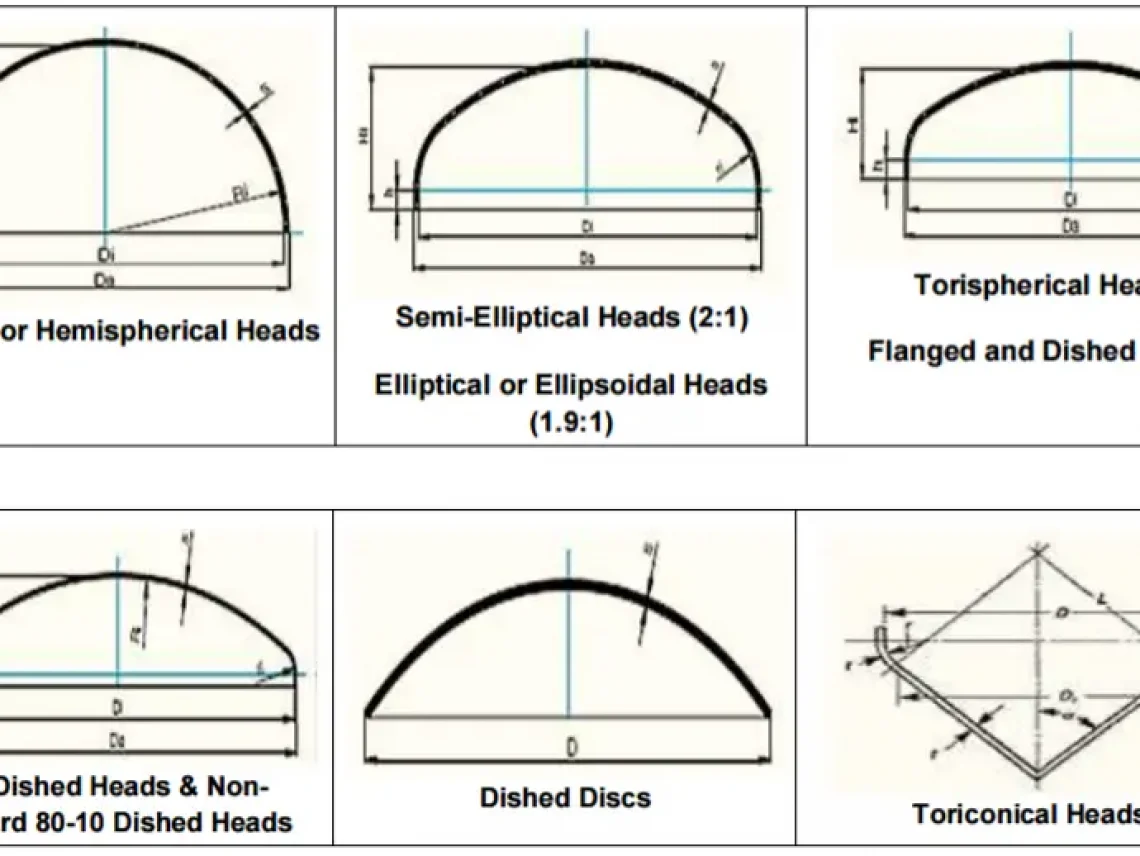
ToggleThere are four main pressure vessel head types—elliptical (2:1), hemispherical, torispherical (ASME F&D), and flat (dished). Each offers a unique balance of strength, stress distribution, cost, and appearance. Choosing the right one hinges on operating pressure, durability, and manufacturing considerations.
Characteristics:
Elliptical shape with a major axis twice the minor.
Smooth stress transition from the shell—minimizes stress points.
Strong structural integrity, making them ideal for high-pressure use.
Applications:
Used in boilers, heat exchangers, and tanks across petrochemical and power generation industries.
Characteristics:
Semi-spherical geometry for even stress distribution.
Excellent strength-to-volume ratio.
Applications:
Frequently found in nuclear and autoclave vessels due to high-pressure tolerance.
Learn more about how this design supports custom fabrication in complex applications.
Characteristics:
Combines a spherical crown with a knuckle radius.
Balanced cost and pressure performance.
Applications:
Popular in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food-processing settings.
For real-world implementation, explore Red River’s prefabricated spool assemblies which often incorporate ASME-compliant heads.
Characteristics:
Simplest and most cost-effective design.
Best suited for low or atmospheric pressure conditions.
Applications:
Common in silos and storage tanks. Great for bulk material handling with minimal pressure exposure.
These are frequently used in skid package systems where pressure demands are minimal but manufacturing efficiency is key.
Educational Note: Flat heads are listed by ASME standards for use cases involving minimal internal pressure.
Different types of pressure vessel heads are designed to meet specific needs and functions. For instance, hemispherical heads offer the best resistance to pressure, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Ellipsoidal heads, on the other hand, are often used when height constraints are a concern, as they have a lower profile than hemispherical heads. Torispherical heads are commonly used for their cost-effectiveness and are suitable for moderate pressure conditions. Flat heads, while not as common due to their lower pressure tolerance, are used in applications where internal pressure is minimal.
The durability and maintenance requirements of a pressure vessel significantly depend on the type of head used. Hemispherical heads, with their even stress distribution, tend to have longer lifespans and lower maintenance needs. Ellipsoidal and torispherical heads, while durable, may require more frequent inspections, particularly at the knuckle regions where stress concentrations can occur. Flat heads are generally less durable under pressure and might need more regular maintenance checks to ensure integrity, especially in applications involving cyclic pressure variations.
Yes, the type of head can impact the cost of a pressure vessel. Hemispherical heads, while offering excellent durability and pressure resistance, are typically more expensive due to their complex manufacturing process. Torispherical heads are often more cost-effective due to their simpler design and easier fabrication process. Ellipsoidal heads strike a balance between performance and cost. The choice of head should consider both the initial fabrication cost and the long-term maintenance expenses.
The choice of material for a pressure vessel head depends on the application, pressure requirements, and the type of head. For high-pressure applications, especially with hemispherical heads, materials with high tensile strength and ductility, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, are preferred. For lower pressure applications, where flat heads might be used, materials like aluminum can be sufficient. The corrosive nature of the contents and operating temperature also play a crucial role in material selection.
Regulations and standards such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code significantly influence the design and selection of pressure vessel heads. These standards ensure safety, reliability, and efficiency by specifying design criteria, material selection, fabrication processes, and testing requirements. Compliance with these standards is crucial, not only for legal and safety reasons but also for ensuring the vessel’s performance and longevity. The type of head must meet the specific requirements set forth for the intended application and operating conditions.
Elliptical heads: Compact and strong—perfect for high-pressure vessels.
Hemispherical heads: Premium strength and longevity—at higher cost.
Torispherical heads: Versatile and budget-friendly for most designs.
Flat heads: Economical choice for non-pressurized systems.
All must comply with regulatory codes like ASME BPVC Section VIII to ensure safety and reliability.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn the realm of industrial solutions, Red River emerges as a pioneer, offering a diverse range of custom-engineered products and facilities. Among our specialties is the design and production of Custom/OEM Pressure Vessels, meticulously crafted to meet individual client requirements, ensuring performance under various pressure conditions. Our expertise extends to the domain of prefabrication, where Red River leads with distinction.
The company excels in creating prefabricated facilities, modules, and packages, reinforcing its stance as a forerunner in innovation and quality. This proficiency is further mirrored in their Modular Skids offering, where they provide an array of Modular Fabricated Skid Packages and Packaged equipment. Each piece is tailored to client specifications, underlining their commitment to delivering precision and excellence in every project they undertake.