Selecting the right pressure vessel head is paramount for ensuring both safety and operational efficiency. An improperly selected head can lead to catastrophic failures, resulting in safety hazards, environmental damage, and significant financial losses. Correct head design ensures the vessel can withstand the intended pressure and temperature without deformation or rupture.
Moreover, the design of the head directly impacts the pressure vessel’s overall performance and lifespan. For example, a well-designed head distributes stress evenly, which in turn minimizes the risk of fatigue and cracking, ultimately extending the vessel’s service life. In contrast, a poorly designed head can create stress concentrations, which can lead to premature failure and significantly reduce the vessel’s lifespan.
Several factors must be considered when selecting a pressure vessel head, including the following:
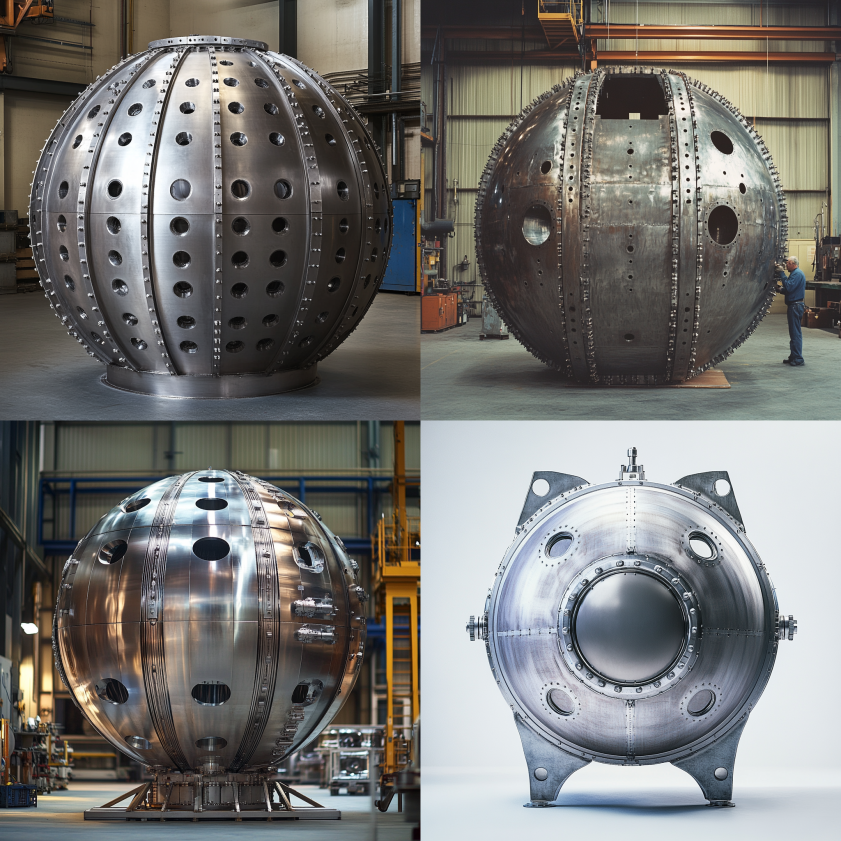

Hemispherical heads are shaped like half of a sphere. They are characterized by their uniform curvature, which provides exceptional strength and makes them highly resistant to pressure. Furthermore, the shape allows for even distribution of stress across the entire head, minimizing the risk of stress concentrations.
The primary advantage of hemispherical heads is their ability to withstand high pressure relative to their thickness. As a result, they are ideal for high-pressure environments such as nuclear reactors, gas storage tanks, and deep-sea submersibles. Their symmetrical shape is inherently strong.
However, it is important to note that hemispherical heads are often more expensive and complex to manufacture than other types. The deep-drawing process and specialized tooling required for their fabrication contribute to the higher cost. Additionally, they often require more welding due to their complex geometry.

Elliptical heads, also known as ellipsoidal heads, feature a semi-elliptical shape. They offer a good compromise between strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of manufacturing. The most common type is the 2:1 elliptical head, where the major axis is twice the length of the minor axis.
The benefits of elliptical heads include a good balance between strength and cost. They are stronger than torispherical or conical heads but less expensive and easier to manufacture than hemispherical heads. Their shape allows for a relatively uniform distribution of stress.
Elliptical heads are widely used in various industries for medium-to-high-pressure applications. They are commonly found in chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and gas pipelines. The 2:1 ratio is considered a standard because it provides a good balance of strength and ease of fabrication.
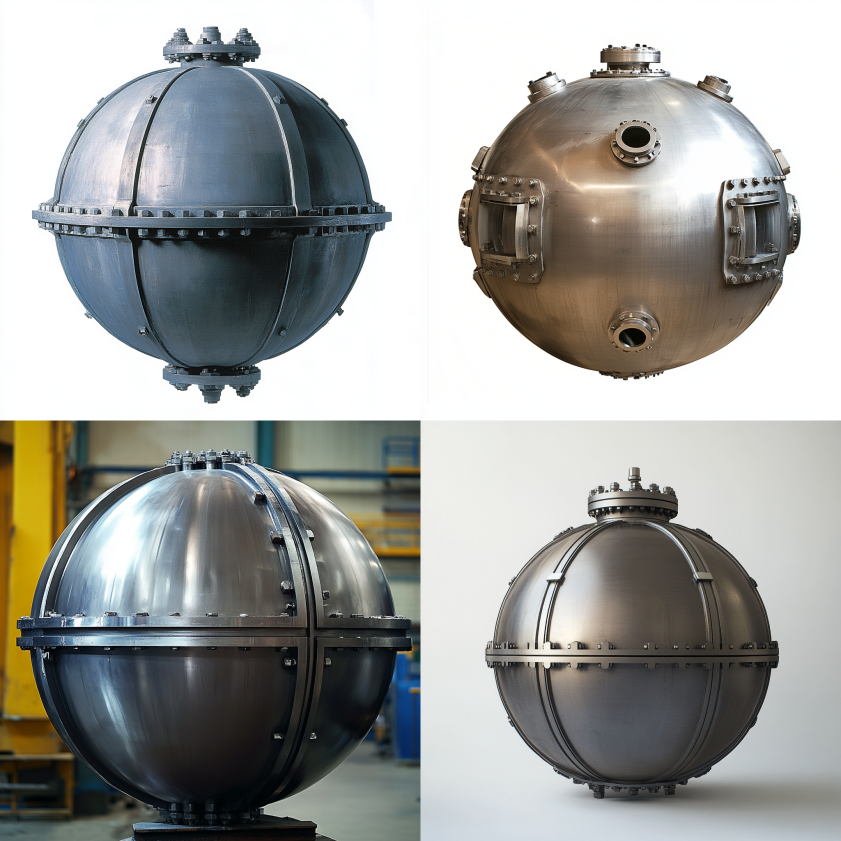

Torispherical heads have a more complex shape than hemispherical or elliptical heads. They consist of a spherical cap (crown radius) and a toroidal section (knuckle radius) that connects the spherical cap to the cylindrical shell.
The main advantages of torispherical heads are their versatility and lower cost compared to hemispherical or elliptical heads. Consequently, they are easier to manufacture and install, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. The design helps reduce stress concentrations at the junction between the head and the shell.
Torispherical heads are commonly used in boilers, storage tanks, and other moderate-pressure vessels. They are an excellent option when high strength is not a primary requirement but cost and ease of manufacturing are important considerations. In some cases, they may require thicker walls compared to hemispherical or elliptical heads to achieve the same level of pressure resistance.
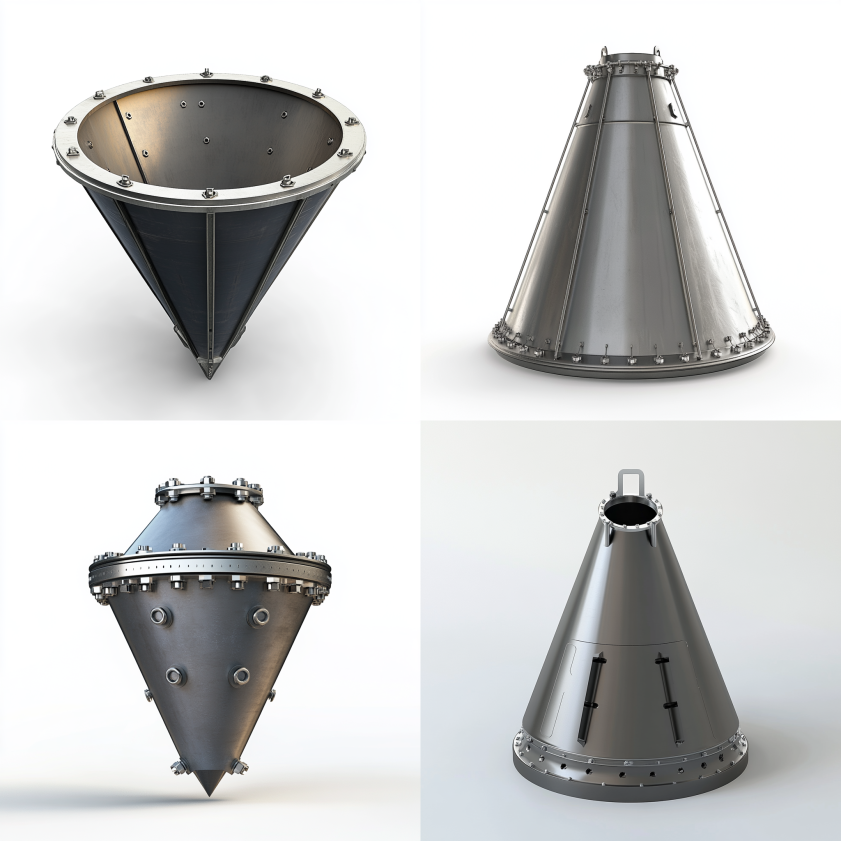

Conical heads are shaped like a cone and are typically used for transitioning between different diameters or supporting structures. The cone angle is a critical parameter in their design.
The primary advantage of conical heads is their ability to facilitate transitions between sections of a pressure vessel with different diameters. Furthermore, they are useful for supporting structures or equipment mounted on the vessel. These heads are commonly found in hoppers, silos, and vessels requiring a gradual change in diameter.
Conical heads may require reinforcement, especially at the junction with the cylindrical shell, depending on the cone angle and pressure. The steeper the cone angle, the greater the stress at the junction. As a result, reinforcement rings or thicker materials may be necessary to ensure structural integrity.
Choosing the right pressure vessel head is a multifaceted decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. From the unparalleled strength of hemispherical heads to the versatile and cost-effective torispherical options, each design offers unique advantages suited to specific applications. Therefore, understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of pressure vessel systems across a wide range of industries. Properly selecting the best head for the task is not just important—it is a vital step in the vessel’s overall design.
Red River specializes in the design and manufacturing of pressure vessels. We also fabricate related items such as prefabricated spools and skid packages.
Reach out to us today and experience the Red River difference. Where American-made products and American Values come together, we care more.
Several factors, such as pressure, temperature, material, application, cost, and manufacturing complexity, all play a significant role in the selection process.
Hemispherical heads, in fact, offer the highest strength-to-weight ratio, making them the strongest option for high-pressure applications.
The key distinction is that elliptical heads have a semi-elliptical shape, whereas torispherical heads feature both a crown radius and a knuckle radius, providing a different structural design.
Generally speaking, conical heads are not ideal for high-pressure environments. However, they can be used for such purposes with additional reinforcement to ensure safety.
The standard ratio for elliptical heads is, typically, 2:1, which is widely recognized as providing a good balance between strength and manufacturing feasibility.
Torispherical heads are often favored due to their excellent balance between cost, versatility, and strength, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Conical heads are commonly employed in hoppers, silos, and other vessels where a transition between diameters is required. Additionally, they are used in various applications where gradual changes in shape are needed.
In the realm of industrial solutions, Red River emerges as a pioneer, offering a diverse range of custom-engineered products and facilities. Among our specialties is the design and production of Custom/OEM Pressure Vessels, meticulously crafted to meet individual client requirements, ensuring performance under various pressure conditions. Our expertise extends to the domain of prefabrication, where Red River leads with distinction.
The company excels in creating prefabricated facilities, modules, and packages, reinforcing its stance as a forerunner in innovation and quality. This proficiency is further mirrored in their Modular Skids offering, where they provide an array of Modular Fabricated Skid Packages and Packaged equipment. Each piece is tailored to client specifications, underlining their commitment to delivering precision and excellence in every project they undertake.