Table of Contents
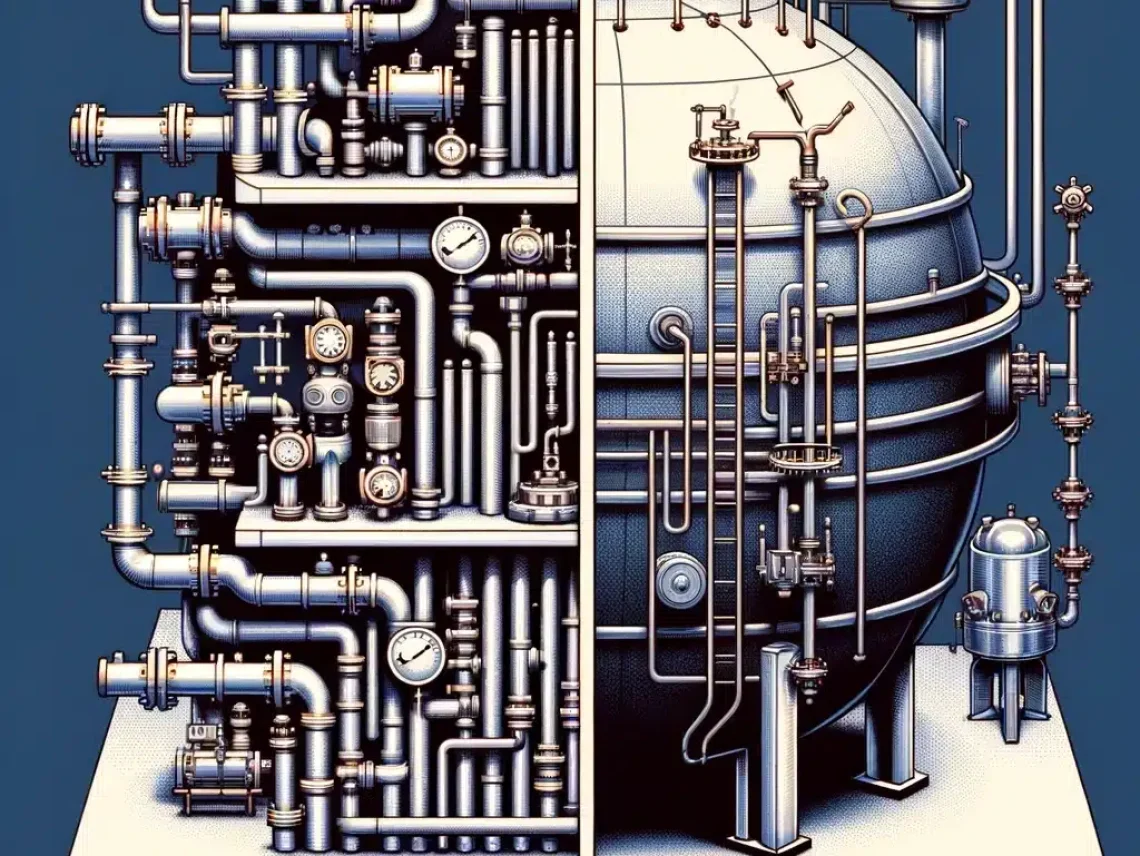
TogglePressurized piping systems are critical to industries like power generation and manufacturing, handling high-pressure fluids and gases under strict safety codes like ASME B31.3. Unlike regular piping, these systems demand robust materials, expert welding, and constant inspections to prevent catastrophic failures. They differ from pressure vessels, which are built to contain pressure rather than transport it. Understanding these systems is vital for safety, compliance, and efficiency. Red River LLC brings decades of expertise to help you design, build, and maintain them the right way.
In today’s industrial landscape, pressurized piping is the silent workhorse behind power plants, refineries, and countless manufacturing processes. Unlike regular pipes, pressurized piping systems are engineered to move fluids or gases at high pressure requiring strict compliance with safety codes such as ASME B31.3. At Red River LLC, we believe in delivering not just compliant but exceptional solutions, leveraging decades of experience in both pressurized piping and pressure vessels.
Understanding the core differences and safety protocols of these systems can save lives, reduce costs, and optimize performance. This guide will clarify everything you need to know so you can make smart, safe, and future-ready decisions.
Pressurized piping refers to a specialized system of pipes, valves, and fittings that transport fluids or gases under significant pressure. Unlike basic plumbing, these systems require engineered supports, leak-proof joints, and continuous monitoring. According to Wikipedia, such piping networks are foundational for process industries worldwide.
Moreover, these systems must pass rigorous testing and inspections. For instance, high-pressure steam piping demands not only robust materials like carbon steel or alloy steel but also precise welding techniques and quality control ensuring everything operates within legal and safety standards.
Transitioning to safety, it’s vital to note that accidents in pressurized piping can result in catastrophic consequences. That’s why Red River LLC meticulously applies safety codes and routine inspections, as highlighted in our in-depth piece on boilers and fired pressure vessels.
When it comes to design, the ASME B31.3 Process Piping code stands out as the industry benchmark. You’ll find it referenced globally, along with related standards like the EU Pressure Equipment Directive (PED), which governs European installations.
Furthermore, materials selection is anything but random. Engineers choose carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys for their ability to withstand high pressure and corrosion. Proper material selection is essential not just for longevity but for legal compliance as well. In-depth requirements for welding and material testing are available in the List of welding codes on Wikipedia.
Routine pressure testing often involving hydrostatic or pneumatic tests ensures that the entire network is robust and leak-free before being commissioned. This multi-layered approach to safety is also mirrored in our practices around steam turbine systems.
Although often grouped together, pressurized piping and pressure vessels have distinct roles in industrial settings. While pressurized piping is all about moving substances safely from one point to another, pressure vessels are designed to hold liquids or gases at a fixed pressure.
From a code perspective, piping is governed by ASME B31 codes, whereas pressure vessels must comply with the ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC). This distinction is crucial for facility owners, operators, and engineers. If you want to see more about how these differences play out, explore our dedicated articles on pressure vessel vs high-pressure vessel and pressure vessel vs column.
Additionally, design priorities differ: piping focuses on flow and connectivity, while vessels emphasize containment and inspection access. Understanding both sides helps ensure your facility’s compliance and efficiency.
In summary, mastering the art and science of pressurized piping is non-negotiable for modern industry. Choosing the right materials, applying the right standards, and understanding the difference from pressure vessels ensures not just compliance but also longevity and cost savings. To keep learning and protect your operations, check out our resource on surge vessel vs pressure vessel.
Partner with Red River LLC for expert-engineered pressurized piping and pressure vessel solutions. Our commitment to quality, safety, and American values ensures your project is in the best hands. Contact us today and see how we can help transform your facility’s performance.
Pressurized piping is a system engineered to move fluids or gases at high pressures, using certified materials and following strict safety standards like ASME B31.3. These systems are essential in high-stakes environments such as chemical plants, power stations, and refineries, where failure can lead to severe safety and operational consequences.
Standard piping usually deals with low-pressure applications and simple layouts. In contrast, pressurized piping is designed for much higher pressure, with robust supports, welded joints, and frequent inspections to withstand thermal expansion, vibration, and corrosive environments.
In the U.S., ASME B31.3 is the main standard, while the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) applies in Europe. These codes define requirements for design, fabrication, testing, and inspection to ensure long-term safety and regulatory compliance.
The most common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels. Selection is based on pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance, and compatibility with the transported substance to prevent material degradation or failure.
ASME BPVC is primarily for pressure vessels, not piping, but it’s often relevant when both systems interact within a facility. For example, if a pressure vessel feeds into a pressurized piping system, both codes must work in tandem for safe integration.
Inspections detect potential failures before they escalate, safeguarding workers and property. They also help maintain system efficiency, extend equipment lifespan, and ensure ongoing code compliance during the operational lifecycle. Learn more about inspection protocols in our comprehensive guide.
Common risks include corrosion, weld cracks, overpressure incidents, and thermal expansion. Without proactive monitoring and maintenance, these issues can lead to costly downtime or catastrophic accidents.
See our deep-dive on pressure vessels vs columns for further insights. It covers functional differences, design implications, and how each component fits into larger industrial systems.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn the realm of industrial solutions, Red River emerges as a pioneer, offering a diverse range of custom-engineered products and facilities. Among our specialties is the design and production of Custom/OEM Pressure Vessels, meticulously crafted to meet individual client requirements, ensuring performance under various pressure conditions. Our expertise extends to the domain of prefabrication, where Red River leads with distinction.
The company excels in creating prefabricated facilities, modules, and packages, reinforcing its stance as a forerunner in innovation and quality. This proficiency is further mirrored in their Modular Skids offering, where they provide an array of Modular Fabricated Skid Packages and Packaged equipment. Each piece is tailored to client specifications, underlining their commitment to delivering precision and excellence in every project they undertake.